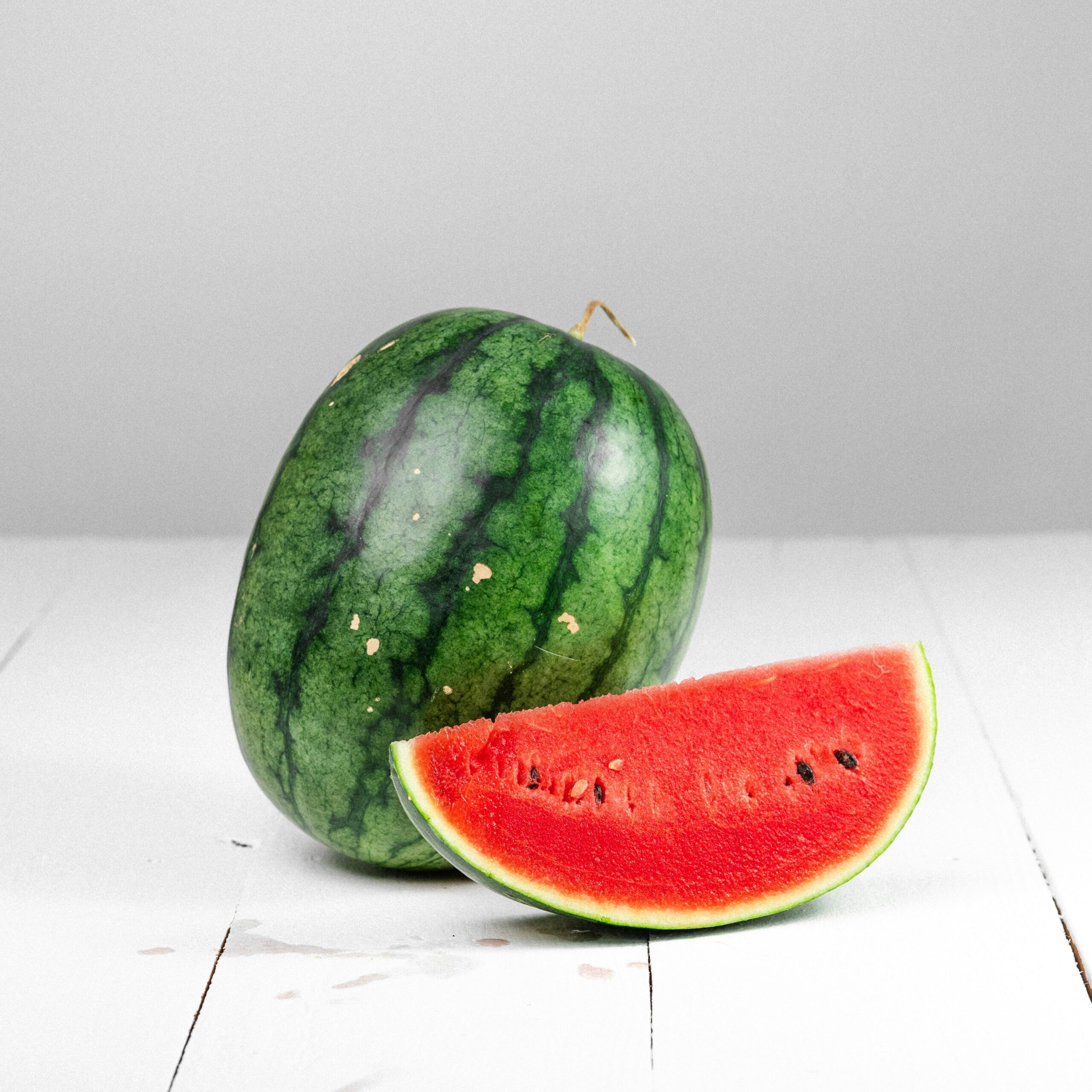
Watermelon is the ultimate summer fruit, and it thrives in warm, sunny conditions. If you’ve ever wondered why some watermelons are sweeter and juicier than others, the secret lies in the climate. A perfect combination of heat, sunlight, and the right soil can make all the difference in growing a delicious watermelon. Let’s explore what makes an ideal climate for watermelon farming!
Warm Temperatures: The Key to Sweet Watermelons
Watermelons love the heat! They grow best in temperatures between 21°C to 35°C (70°F to 95°F). If the weather is too cold, the seeds won’t germinate properly, and the plant’s growth will slow down. On the other hand, if it gets too hot (above 40°C or 104°F), the vines might suffer from heat stress, reducing fruit quality.
For the best results, watermelons should be planted after the last frost when the soil temperature reaches 18°C (65°F) or higher. The warmer the soil, the faster the seeds will sprout, and the stronger the vines will become. If you’re in a cooler climate, you might need black plastic mulch to warm up the soil and give your watermelon plants a head start.
Sunshine: The More, The Better!
If you want your watermelons to grow big and sweet, they need at least 8 to 10 hours of full sun daily. These plants love basking in the sunlight, which helps them produce the natural sugars that make the fruit taste amazing. Without enough sunshine, the vines may grow weak, and the fruit may lack flavor.
That’s why watermelons thrive in tropical and subtropical regions. Countries like India, Mexico, and Egypt produce some of the best watermelons because they have long, sunny days and warm temperatures. If you’re growing watermelons in a cooler area, choose a south-facing spot in your garden to maximize sunlight exposure.
Low Humidity and Moderate Rainfall: Finding the Balance
Watermelons need water, but too much moisture can cause problems. Ideally, they require 25 to 50 cm (10 to 20 inches) of rainfall during the growing season. While regular watering is essential, especially when the vines are developing, excessive rain or high humidity can lead to fungal diseases and rot.
The best climate for watermelon growth has a dry, warm environment with controlled irrigation. Drip irrigation is a great way to keep the soil consistently moist without overwatering the plants. If you live in a humid area, make sure to space out the plants well to improve airflow and prevent disease.
The Best Regions for Watermelon Cultivation
Watermelons are grown in many parts of the world, but some regions are just perfect for their cultivation. In the United States, states like Texas, Florida, and California produce massive amounts of watermelons because they have the right mix of warmth, sunlight, and moderate rainfall. In India, states like Rajasthan, Maharashtra, and Karnataka are known for their premium-quality watermelons. Other major producers include China, Brazil, Iran, and Turkey, where the climate naturally supports watermelon farming.

How Farmers Ensure Quality & Size in Their Crops
Ever wondered how farmers manage to grow those perfectly shaped, deliciously fresh fruits and vegetables? It’s not just luck—it’s a science! Behind every high-quality crop is a dedicated farmer who carefully monitors everything from soil health to watering schedules. If you’ve ever bitten into a juicy watermelon or admired a flawless tomato, know that a farmer worked hard to ensure it reached you in perfect condition.
Let’s take a deep dive into how farmers ensure quality and size in their produce!
Selecting the Right Seeds: It All Starts Here
Every great harvest starts with the right seeds. Farmers carefully choose high-quality, disease-resistant seed varieties that promise good yield, size, and taste. They don’t just pick any seed—they research which ones are best suited for their soil type, climate, and market demand.
Seed selection is like picking players for a sports team—only the strongest and healthiest make the cut. Many farmers opt for hybrid seeds that are designed to grow faster, resist pests, and produce bigger fruits and vegetables. Some even work with agricultural scientists to develop better seed varieties that will thrive in different weather conditions.
Soil Health: The Foundation of High-Quality Crops
Healthy soil is the secret to strong, well-sized produce. Farmers regularly test their soil to check for nutrients, pH balance, and moisture levels. If the soil lacks key nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus, or potassium, they add organic compost or natural fertilizers to restore balance.
Many farmers practice crop rotation to keep the soil rich and prevent nutrient depletion. For example, after harvesting one type of crop, they plant another that helps replenish the soil, reducing the need for artificial fertilizers. This method ensures that plants get the best possible nutrition for steady growth and optimal size.
The Perfect Balance of Water & Sunlight
Just like humans need food and water to grow strong, plants need a balanced mix of sunlight and irrigation. Farmers closely monitor rainfall and temperature to ensure crops receive the right amount of moisture without drowning or drying out.
Many use drip irrigation systems to deliver water directly to the roots, preventing wastage and ensuring deep hydration. Too much water can cause plants to grow too fast and lose their firmness, while too little water can result in stunted, smaller produce. Smart farming techniques help maintain the perfect balance, giving you the freshest, juiciest fruits and vegetables.
Pest & Disease Control: Keeping the Crops Safe
No farmer wants to see months of hard work ruined by pests or diseases. To keep crops healthy, they use a combination of natural pest control methods, including companion planting, organic pesticides, and biological pest management.
For example, farmers may plant marigolds around their crops because these flowers naturally repel insects. They also introduce friendly insects like ladybugs, which eat harmful pests without damaging the plants. By reducing chemical pesticide use, farmers protect both their crops and the environment.
Pruning & Thinning: Helping Crops Grow Bigger
Farmers don’t just plant and wait—they actively manage plant growth to ensure the best results. Pruning involves cutting off weak or excess branches so the plant can focus its energy on growing bigger, better fruits and vegetables.
Another technique is thinning, where farmers remove smaller or weaker fruits to allow the remaining ones to grow larger. This is common in watermelon, apple, and grape farming, where quality is often more important than quantity. A plant can only provide so many nutrients, so by reducing competition, farmers ensure that each fruit reaches its maximum potential.
Harvesting at the Right Time: Timing is Everything
Picking fruits and vegetables at the right stage of ripeness is crucial. If harvested too early, they may not develop their full flavor and size. If picked too late, they might overripen and lose quality.
Farmers use sugar content tests, color changes, and even simple touch techniques to decide when to harvest. Some crops, like mangoes and bananas, are picked slightly unripe so they can ripen naturally during transport, ensuring they reach consumers at peak freshness.

Organic vs. Conventional Farming: Which Grows the Best Watermelons?
Watermelons are a summer favorite, but do you know how different farming methods affect their taste, size, and quality? Organic and conventional farming take very different approaches to growing this juicy fruit. Let’s explore how each method impacts the watermelons you enjoy!
Growing Watermelons the Organic Way
Organic watermelon farming focuses on natural methods to enhance soil health and fruit quality. Farmers avoid synthetic fertilizers and pesticides, using compost, animal manure, and crop rotation to enrich the soil. These techniques help produce watermelons with a natural sweetness and vibrant color.
In organic farms, pest control is done using natural predators, neem-based sprays, and intercropping with companion plants. This ensures that the fruit remains free from harmful chemicals while still being protected from insects. The result? A pure, refreshing watermelon that’s as close to nature as possible.
Since organic farming relies on natural soil nutrients, organic watermelons often take a little longer to grow. They might not always be as large as conventionally grown ones, but they make up for it with their intense flavor and high nutrient content.
Another advantage of organic watermelon farming is its environmental impact. By avoiding chemical runoff, organic farms help maintain healthier soil and cleaner water sources, making them a great choice for sustainability-conscious consumers.
How Conventional Farming Grows Watermelons Faster
Conventional farming methods focus on high yield and efficiency. Farmers use synthetic fertilizers to boost plant growth, ensuring larger watermelons in a shorter time. These fertilizers provide the essential nutrients directly to the soil, allowing the plants to grow rapidly and produce consistently sized fruit.
To protect crops from pests and diseases, conventional farmers use pesticides and fungicides. This helps reduce fruit loss and ensures that watermelons stay fresh longer during transportation. However, residue from these chemicals can sometimes remain on the fruit, which is why washing before consumption is important.
Irrigation techniques in conventional farming are highly advanced. Drip irrigation and plastic mulching help conserve water while ensuring each watermelon gets the perfect amount of hydration. This method produces firm, juicy watermelons that are ready to hit the market quickly.
Because conventional farms operate on a large scale, they can supply watermelons year-round. While organic farming may depend on seasonal cycles, conventional methods allow farmers to meet high demand without interruption.
Taste, Size, and Nutritional Differences
When it comes to taste, organic watermelons are often described as having a richer, more natural sweetness. The slower growing process allows the fruit to develop deep flavors, making each bite more refreshing. On the other hand, conventionally grown watermelons tend to be larger and more uniform in size, thanks to controlled fertilizers and growth boosters.
Nutritionally, organic watermelons may contain slightly higher levels of antioxidants and vitamins, as they grow in healthier, chemical-free soil. However, both organic and conventional watermelons remain an excellent source of hydration, vitamin C, and lycopene.
If you prefer a more natural, earth-friendly fruit, organic watermelons are the way to go. But if size and availability are your priorities, conventionally grown watermelons offer a reliable choice.

Sustainable Farming Practices for Better Yields
Farming has come a long way, but one thing remains the same—healthy crops need healthy soil, water, and care. With increasing demand for food and climate change knocking on our doors, sustainable farming is more important than ever. If you’re a farmer looking to boost your yields while keeping the environment happy, this guide is for you!
1. Soil Health: The Secret to a Thriving Farm
Think of soil as the foundation of farming. If it’s rich in nutrients, your crops will flourish. Sustainable farmers focus on soil regeneration rather than just extracting nutrients. One great way to do this is through crop rotation—planting different crops in the same field over time. This prevents soil exhaustion and naturally controls pests.
Another trick? Cover crops like legumes and clover! These plants improve soil fertility by adding nitrogen and preventing erosion. Instead of relying on chemical fertilizers, sustainable farmers use compost, manure, and biofertilizers to keep the soil alive and well. The healthier the soil, the better your harvest!
2. Smart Water Management: Every Drop Counts
Water is a precious resource, and using it wisely is key to sustainable farming. Traditional irrigation methods often waste more water than they provide to crops. That’s where drip irrigation comes in! This method delivers water directly to plant roots, reducing waste and ensuring crops get exactly what they need.
Another great practice is rainwater harvesting—collecting and storing rainwater for later use. Farmers can use ponds, tanks, or underground storage systems to keep extra water for dry seasons. Mulching (covering soil with straw or organic material) also helps retain moisture, reducing the need for frequent watering. By conserving water, you not only help the environment but also reduce farming costs!
3. Natural Pest Control: Winning Without Chemicals
Nobody likes pests ruining a good harvest, but relying on chemical pesticides can harm the soil, water, and beneficial insects. Sustainable farmers use integrated pest management (IPM)—a mix of natural methods to keep pests away without harming the environment.
Introducing predator insects like ladybugs and praying mantises can keep harmful bugs in check. Companion planting—growing certain plants together—also helps. For example, planting marigolds alongside vegetables repels insects naturally. Organic sprays made from neem oil or garlic extracts work wonders without leaving toxic residues.
With these natural pest control methods, you can protect your crops while keeping your farm ecosystem balanced and healthy.
4. Diversification: The More, The Merrier
Relying on just one crop can be risky. If disease strikes or market prices drop, your entire farm could suffer. That’s why crop diversification is a game-changer. By growing multiple crops, farmers reduce their risks and improve soil fertility.
Many sustainable farms also incorporate agroforestry—planting trees and shrubs alongside crops. This not only improves biodiversity but also provides additional income sources like fruits, nuts, or timber. If you’re farming livestock, consider mixed farming, where animals and crops coexist, helping each other thrive. The more variety on your farm, the more resilient it becomes!
5. Organic Fertilizers & Composting: Nature’s Superfood for Plants
Instead of synthetic fertilizers that degrade soil over time, sustainable farmers use organic fertilizers like compost, manure, and biofertilizers. Composting farm waste, food scraps, and plant residues creates a natural, nutrient-rich soil booster that keeps crops strong and healthy.
Vermicomposting—using earthworms to break down organic matter—produces one of the best natural fertilizers available. Biofertilizers made from beneficial bacteria and fungi help plants absorb nutrients efficiently. Not only do these methods improve crop yields, but they also reduce pollution and keep the soil alive.

Conclusion: Growing the Best Watermelons with Smart Farming
The journey to cultivating perfect watermelons starts with the right climate. A balance of warm temperatures, plenty of sunlight, and well-drained soil ensures a healthy and productive crop. Without these conditions, achieving high yields and great taste becomes a challenge.
Farmers go the extra mile to maintain quality and size by using selective breeding, monitoring soil health, and ensuring proper spacing for each plant. With these techniques, they consistently produce watermelons that are sweet, juicy, and uniform in size—meeting market expectations.
When it comes to organic vs. conventional farming, both methods have their strengths. Organic farming focuses on sustainability and chemical-free produce, while conventional farming leverages advanced fertilizers and pest control for higher yields. The best approach often combines the benefits of both to meet global demand efficiently.
Sustainable farming is the key to a future-proof industry. By conserving water, using crop rotation, and reducing chemical reliance, farmers can ensure long-term productivity. A shift towards eco-friendly practices benefits both the land and consumers, guaranteeing that delicious, high-quality watermelons continue to reach tables worldwide.